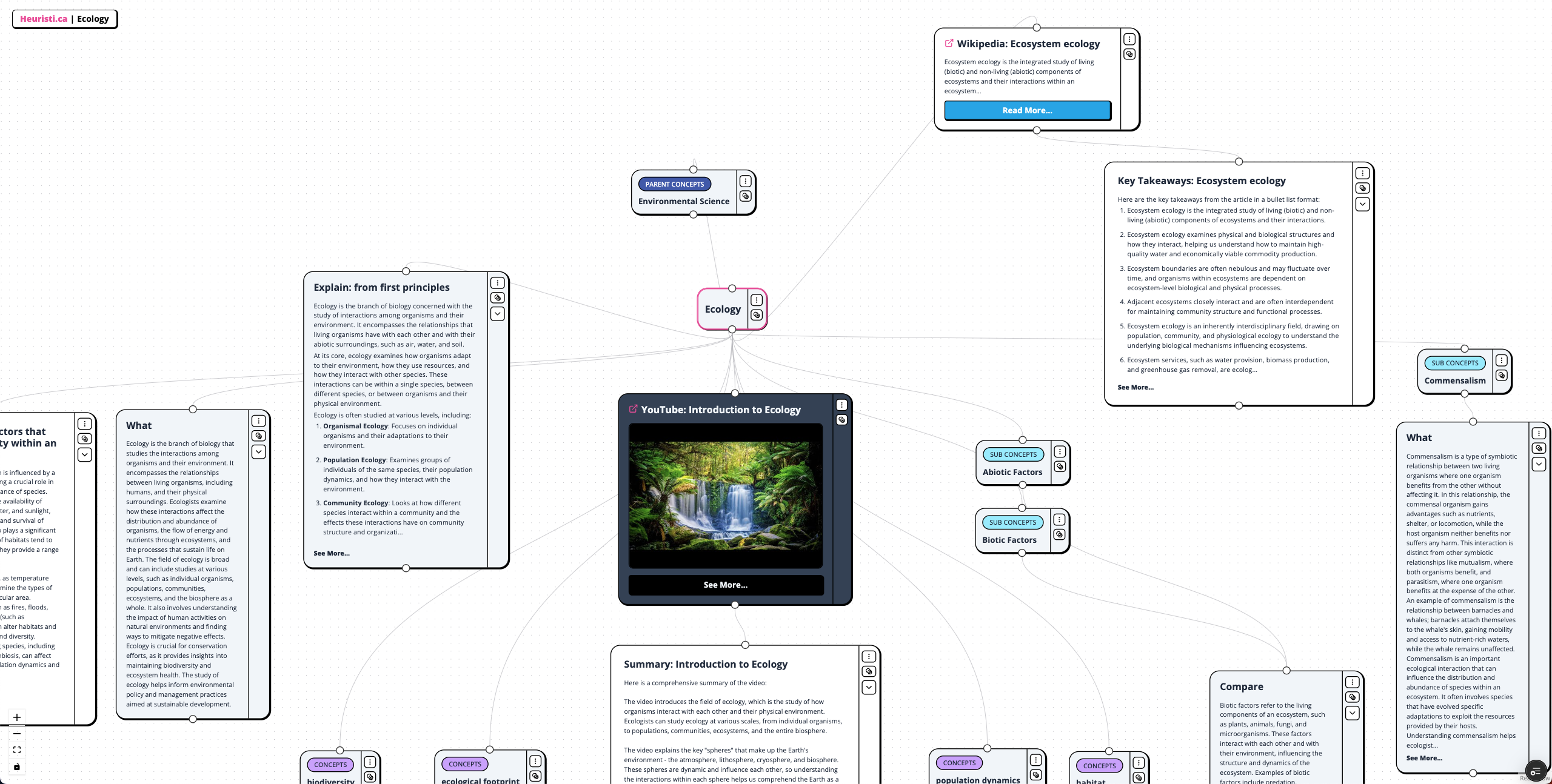
Ecology Concept Map
Summary
Ecology is a branch of biology that focuses on the interactions among organisms and their environment. It studies the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical surroundings, examining how these interactions influence the distribution and abundance of species, energy flow, and nutrient cycling within ecosystems. The field encompasses various levels of study, including individual organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, and the biosphere, and it plays a crucial role in conservation efforts and sustainable development.
Biodiversity
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including different species of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, as well as genetic differences within these species and the ecosystems they form. It is essential for ecosystem health and stability, providing vital services such as pollination, nutrient cycling, and climate regulation. The loss of biodiversity, often driven by human activities like deforestation and pollution, poses significant threats to ecosystems and human societies. Conservation efforts aim to protect and restore biodiversity to ensure the resilience and sustainability of natural systems.
Ecological Footprint
The ecological footprint measures the environmental impact of individuals, communities, or organizations by quantifying the natural resources consumed and waste generated. It is expressed in terms of the land and water area required to sustain those resources and absorb waste. This concept helps assess the sustainability of human activities and highlights the need for more sustainable practices. However, it faces criticism for oversimplifying complex environmental issues and potentially neglecting other important factors.
Population Dynamics
Population dynamics studies how and why populations of organisms change over time, focusing on factors such as birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration. This field is crucial for understanding species growth patterns, interactions with the environment, and the impact of human activities on ecosystems. It informs decisions about biodiversity conservation and resource management.
Biotic and Abiotic Factors
Biotic factors are the living components of an ecosystem, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, while abiotic factors are the non-living physical and chemical components, such as sunlight, temperature, and water. Both types of factors interact and influence each other, shaping the structure and dynamics of ecosystems. Understanding their balance is essential for studying ecosystem health.
Commensalism
Commensalism is a type of symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed. This interaction can influence species distribution and abundance within ecosystems, highlighting the complex interdependencies in natural environments.
Responses to Extreme Changes
Biotic factors respond to extreme changes in abiotic conditions, such as natural disasters, in various ways, including adaptation, migration, population decline, and changes in community structure. Understanding these responses is crucial for conservation efforts, especially in the context of climate change and increasing natural disasters.
Ecosystem Ecology
Ecosystem ecology integrates the study of living and non-living components of ecosystems and their interactions. It examines how physical and biological structures interact, influencing ecosystem services essential for human societies. This interdisciplinary field draws on various ecological principles to understand and manage ecosystems effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Ecology is the branch of biology that studies interactions among organisms and their environment.
- It examines relationships between living organisms and their physical surroundings.
- Ecologists study the distribution and abundance of organisms, energy flow, and nutrient cycling.
- The field includes various levels of study: individual organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, and the biosphere.
- Human activities impact natural environments, necessitating conservation efforts.
- Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, crucial for ecosystem health and stability.
- Biodiversity supports essential services like pollination, nutrient cycling, and climate regulation.
- The loss of biodiversity threatens ecosystems and human societies.
- The ecological footprint measures the environmental impact of individuals or communities.
- It quantifies natural resource consumption and waste generation in terms of land and water area.
- Population dynamics studies how populations change over time due to various factors.
- Biotic factors are living components of ecosystems, while abiotic factors are non-living components.
- Commensalism is a symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits without harming the other.
- Ecosystem ecology integrates biotic and abiotic components to understand ecosystem interactions.
- Ecosystem services are essential for human societies and include water provision and biomass production.