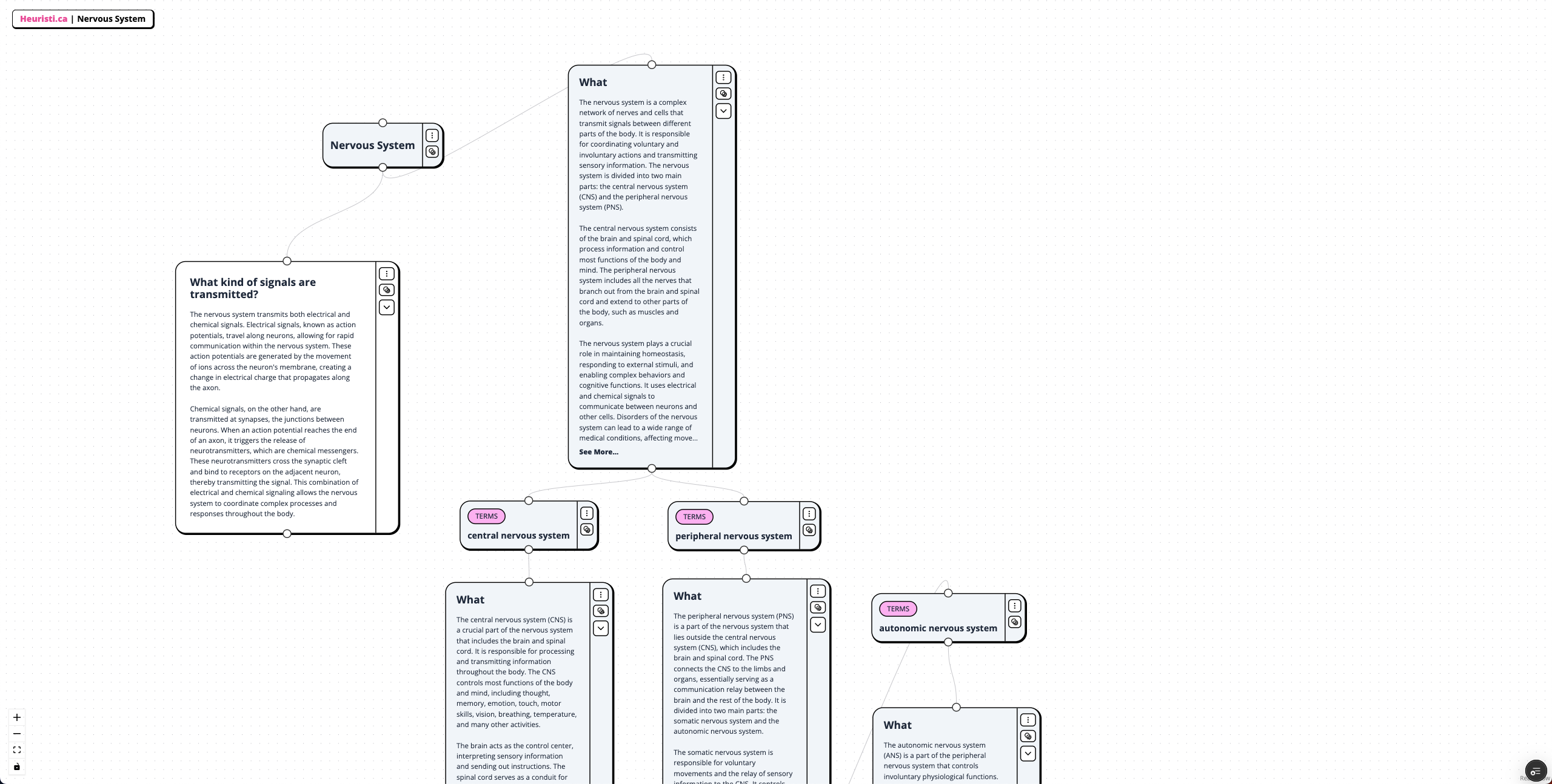
Nervous System Concept Map
The nervous system is a complex network of nerves and cells that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It consists of the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which connects the CNS to the limbs and organs. The CNS processes information and controls most bodily functions, while the PNS regulates voluntary and involuntary actions. The nervous system uses electrical signals, known as action potentials, for rapid communication within the body, and chemical signals at synapses for transmitting messages between neurons. This combination of electrical and chemical signaling enables the coordination of complex processes and responses throughout the body, ensuring appropriate reactions to internal and external stimuli.
Key Takeaways
- The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, controlling most body functions.
- The PNS connects the CNS to limbs and organs, managing voluntary and involuntary actions.
- Electrical signals (action potentials) travel along neurons for rapid communication.
- Chemical signals are transmitted at synapses through neurotransmitters.
- The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements via skeletal muscles.
- Reflex arcs involve sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons, and effectors for rapid responses.
- Disruption in reflex arc components can compromise reflex actions.
- The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion.
- The ANS includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems for balancing responses.
- The "fight or flight" response prepares the body for perceived threats.
- Oxytocin is a hormone crucial for social bonding and reproductive functions.
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, controlling most body functions.
- The PNS connects the CNS to limbs and organs, managing voluntary and involuntary actions.
- Electrical signals (action potentials) travel along neurons for rapid communication.
- Chemical signals are transmitted at synapses through neurotransmitters.
- The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements via skeletal muscles.
- Reflex arcs involve sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons, and effectors for rapid responses.
- Disruption in reflex arc components can compromise reflex actions.
- The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions like heart rate and digestion.
- The ANS includes the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems for balancing responses.
- The "fight or flight" response prepares the body for perceived threats.
- Oxytocin is a hormone crucial for social bonding and reproductive functions.
Additional Concepts
nervous system
neurons
synapses
neurotransmitters
ion channels
electrical signaling
chemical signaling
brain functions
spinal cord functions
sensory receptors
interneurons
reflex actions
reflex pathways
sensory integration
motor responses
autonomic functions
stress responses
hormone release
social bonding
childbirth hormones
hypothalamus functions
empathy behaviors
therapeutic potential
Questions and Answers
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is a complex network of nerves and cells that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It is responsible for coordinating voluntary and involuntary actions and transmitting sensory information.
What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What is the central nervous system (CNS)?
The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord, processing information and controlling most functions of the body and mind.
What is the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) connects the CNS to the limbs and organs, serving as a communication relay between the brain and the rest of the body.
What is the somatic nervous system (SNS)?
The somatic nervous system (SNS) is associated with the voluntary control of body movements via skeletal muscles, crucial for activities requiring conscious thought and intentional movement.
What are reflex arcs?
Reflex arcs are neural pathways that control reflex actions, involving a direct route from sensory neurons to motor neurons to produce quick, involuntary responses to stimuli.
What is the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) controls involuntary physiological functions, regulating activities like heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate.
Flashcards
What is the nervous system?
The nervous system is a complex network of nerves and cells that transmit signals between different parts of the body, coordinating voluntary and involuntary actions and transmitting sensory information.
What are the two main parts of the nervous system?
The nervous system is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
What does the central nervous system consist of?
The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, which process information and control most functions of the body and mind.
What is the role of the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system connects the CNS to the limbs and organs, serving as a communication relay between the brain and the rest of the body.
What is the somatic nervous system responsible for?
The somatic nervous system is responsible for voluntary movements and the relay of sensory information to the CNS.
What are reflex arcs?
Reflex arcs are neural pathways that control reflex actions, involving a direct route from sensory neurons to motor neurons, bypassing the brain for quick responses.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary physiological functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate, operating without conscious control.
What is the 'fight or flight' response?
The 'fight or flight' response is a physiological reaction to perceived threats, preparing the body to either confront or escape from danger.
What is oxytocin and its role?
Oxytocin is a hormone that plays a significant role in social bonding, childbirth, and breastfeeding, often referred to as the 'love hormone' due to its effects on promoting feelings of connection.
What is the 'tend and befriend' response?
The 'tend and befriend' response is a behavioral pattern observed in stressful situations, particularly among females, involving nurturing activities and forming social networks for mutual support.