How to Use Mind Maps for Effective Studying
Mind maps are impactful visual tools that could improve studying by helping with organization and retention of information better. Complex topics can be simplified by a combination of text, visuals, and structure in mind maps, making studying not as boring as it once was.
This article will explain how to use mind maps in studying and give a step-by-step approach in constructing effective study mind maps.
What Are Mind Maps?
Mind maps are the visual displays of ideas, concepts, or information focused around an idea. The basic structure entails placing the most important idea in the center, with subsequent creation of branches for subtopics and details. Each branch speaks to a connection that can provide an easy view into relationships between different pieces of information.
Advantages of Using Mind Maps in Studying
Some of the positive features of mind maps are those that help improve study much more effectively. Visual organization of information in mind maps helps with clarification and understanding of subjects, and with ease of remembering. Such structure, in turn, enables learners to see the relationships of ideas within a given subject matter and hence promote understanding.
Moreover, the use of colors, symbols, and images in mind maps stimulates both parts of the brain, which improves long-term memorization. The mind map supports the encoding of information in more forms due to its visual nature, thus providing easy recall.
Also, in mind maps, students can manage to take notes in a more effective way: it captures the keyword, concept, or connection. This one makes review much easier and quicker, which is beneficial while studying.
The flexible format of a mind map allows creativity and engagement because such format allows students to think out of the box and find new ways of representing information. This flexibility can make studying more agreeable and varied, therefore stimulating interest and further increasing overall learning achievement.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Study Mind Map
First, determine the main area of interest, such as "Photosynthesis" in biology or "Roman Empire" in history. Inscribe your topic in the center of the page or screen.
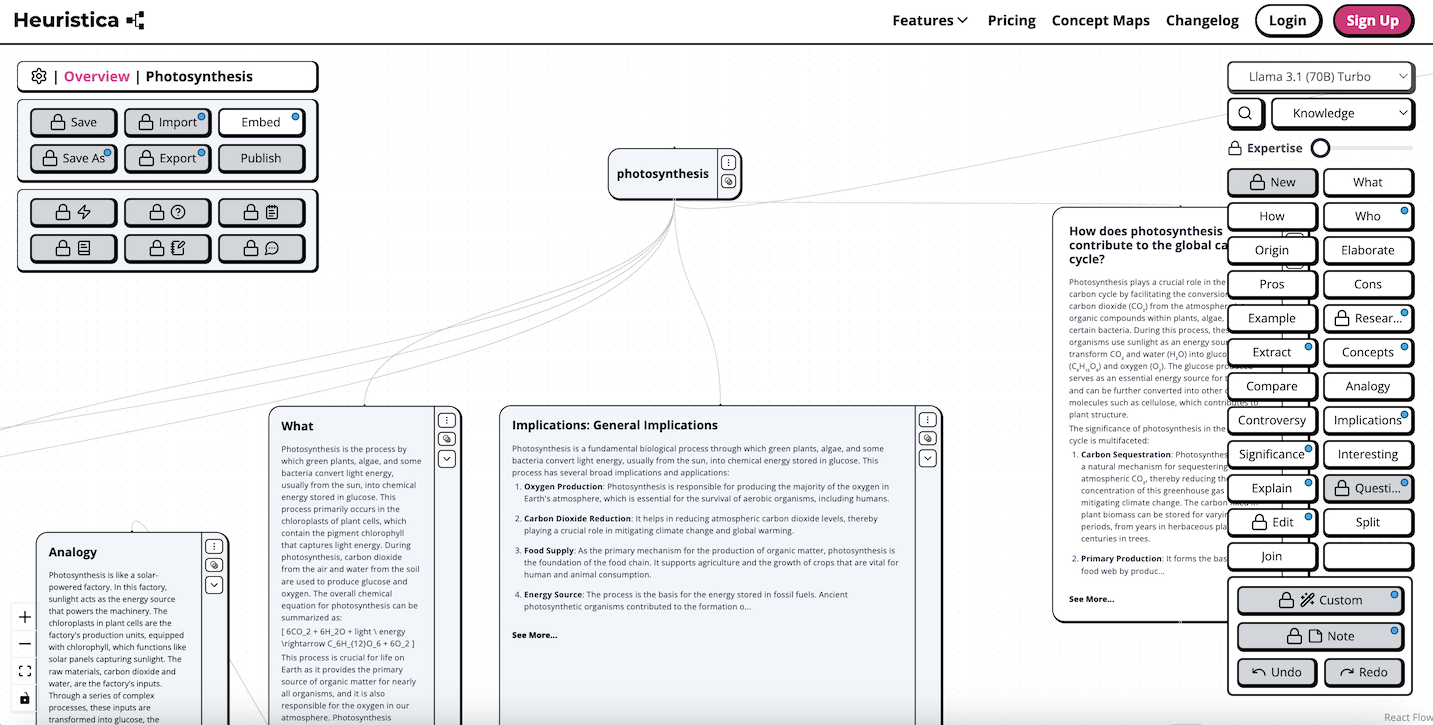 List the main subtopics that concern your central topic. For example, if your central topic researches photosynthesis, then your major branches might be "Chloroplasts," "Light Reactions," "Calvin Cycle," and "Environmental Factors." Write each subtopic out as a separate branch radiating from the center of your paper where you have written your central topic.
List the main subtopics that concern your central topic. For example, if your central topic researches photosynthesis, then your major branches might be "Chloroplasts," "Light Reactions," "Calvin Cycle," and "Environmental Factors." Write each subtopic out as a separate branch radiating from the center of your paper where you have written your central topic.
Under each of those subtopics, create smaller branches with even more information. For example, under "Light Reactions," you could have the branching words "Photosystem I," "Photosystem II," and "ATP Production." This hierarchical approach will allow you to break down any of the more complex subjects down into smaller, manageable chunks.
Use color to differentiate between branches and topics. Incorporating images and icons will make your mind map more interesting, and may even improve memory. For example, you might include an icon of a sun to connect to needing a light for planning a photosynthesis map.
Periodically go back to the mind map and check that you are including all of the major points. Make revisions to make it clearer or add information as you research the topic further.
Best Practices for Mind Mapping
To effectively build mind maps, one should present them in a simple and clear format where one does not clutter and focuses majorly on the key points.
Through sticking to the very essential information and keeping an organized layout, you are assured of easy-to-follow and understandable mind maps. The use of key terms or short phrases on the branches, and not long sentences, helps in directing attention to the key ideas, hence making the map concise. This approach simplifies the content but also helps with quicker review and comprehension.
Besides simplicity, information should be hierarchically organized around one main topic in the center, with subtopics branching from it. That also means that similar ideas are grouped together to better understand and visually perceive how the elements relate.
Incorporate visuals like icons, images, and color codes to enhance memorability even more, adding attractiveness to the mind map. Different colors for various subtopics or the addition of pictures may present which concept is different and provide a visual of the information that is more memorable.
Mind Maps vs. Concept Maps
Mind maps focus on a central issue and expand outward, whereas concept maps have multiple nodes interconnected to illustrate relationships. For example, in a mind map about "Electricity", "Current", "Voltage", and "Resistance" can each be separate branches, while in a concept map, each of these can be connected with other topics like "Ohm's Law" and "Power". Here you can find a more-detailed review of Concept Maps vs Mind Maps.
Mind Map: Digital vs. Hand-Drawn
Each has its strong and weak points: a digital mind map and hand-drawn. Digital mind maps are easily edited, shared, and stored; thus, they are convenient for collaborative work and long-term use. Many digital tools have examples and options of integration linked to other study resources, further enhancing functionality.
They can, however, be devoid of the actual tactile and sensory experience of drawing by hand, which many find conducive to learning. Conversely, hand-drawn mind maps are free to be creative and personalized, as physical writing and sketching tend to reinforce memory. The drawback with such maps is that they can be more cumbersome to edit, update, or share, especially compared with the flexibility afforded by digital versions.
Heuristi.ca: Mind Mapping in the Digital Age
 Heuristi.ca is a concept mapping tool but it can also be an excellent digital mind mapping service. Users can easily create interactive and dynamic mind maps via its very user-friendly interface. It makes adding links, notes and even research papers to the mind map is pretty easy, making it quite suitable for both individual study and group collaboration. The AI-driven suggestions of Heuristi.ca can help expand your mind map with related concepts, thus improving your learning process.
Heuristi.ca is a concept mapping tool but it can also be an excellent digital mind mapping service. Users can easily create interactive and dynamic mind maps via its very user-friendly interface. It makes adding links, notes and even research papers to the mind map is pretty easy, making it quite suitable for both individual study and group collaboration. The AI-driven suggestions of Heuristi.ca can help expand your mind map with related concepts, thus improving your learning process.
Using Mind Maps for Different Study Activities
Mind maps can be used in a variety of study activities, making them very valuable tools to students in terms of improving their learning process. In lectures, mind maps will help to organize the key points to be identified in real-time to avoid being dragged by minute details of the lecture.
Starting with a broad main topic in the center, additions can be made for each major point discussed, showing clearly and in a structured manner what the lecture is discussing.
Supporting details or examples can easily be added using smaller branches to help later in reviewing and connecting ideas with more ease. This approach will not only facilitate active listening but also aid in retaining information more effectively.
Besides note-taking, mind maps are excellent in summarizing the chapters of textbooks, preparation for exams, and even project planning. In dealing with textbooks, this means that, for every chapter of the textbook, there should be a separate mind map where the information to be retained will be summarized down into key sections, which is great for fast comprehension and review of major topics.
In studying for exams, mind maps serve as a type of visual summary of study material whereby the student can focus on key terms and ideas and the relationships among them for a big-picture view. For group projects, the mind map is an excellent tool for planning where tasks can be listed, jobs can be assigned, and timelines can be viewed so all participants know what is expected of them. Mind maps can be applied to all of these activities to make studying more organized, engaging, and productive.
Mind maps could fundamentally change the way you study because they make it a more organized and visually oriented process in which learning becomes interactive. You can create them on the computer or by hand. However you create your mind map, if created effectively, you will comprehend and retain information better to use it.
Similar Posts
How to Make a Concept Map: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
Learn to create effective concept maps with our step-by-step tutorial. Master this powerful visual tool to organize, connect, and communicate ideas.
The Comprehensive Guide to Concept Maps: Their Purpose & Power
Learn about concept maps and their role in organizing and communicating complex information across various fields like education, business, and personal development.
Concept Maps vs Mind Maps: Structural Differences Explained
Discover the structural differences between concept maps and mind maps. Learn how these visual tools organize information to suit your specific needs.


