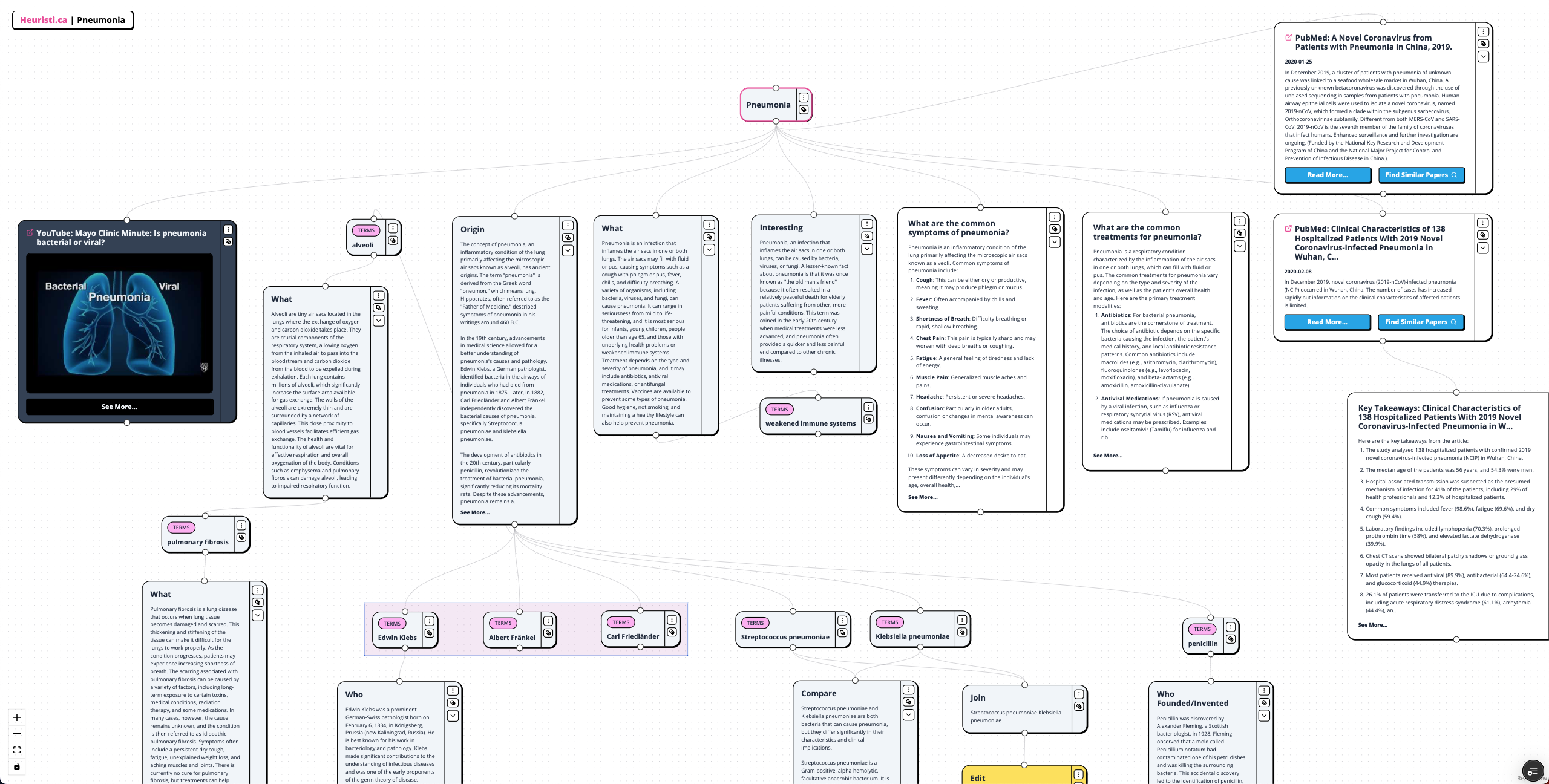
Pneumonia Concept Map
Summary
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus. Symptoms include cough with phlegm, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. Various organisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, can cause pneumonia, which can range from mild to life-threatening, particularly affecting infants, young children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. Treatment varies based on the type and severity of pneumonia and may involve antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antifungal treatments. Preventive measures include vaccines, good hygiene, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Historical Context
The term "pneumonia" originates from the Greek word "pneumon," meaning lung. Hippocrates described pneumonia symptoms around 460 B.C. In the 19th century, significant advancements in understanding pneumonia's causes were made, including the identification of bacteria by Edwin Klebs, Carl Friedländer, and Albert Fränkel. The introduction of antibiotics, particularly penicillin, in the 20th century greatly improved treatment outcomes, although pneumonia remains a major health concern.
Alveoli and Their Role
Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs, allowing oxygen to enter the bloodstream and carbon dioxide to be expelled. They are essential for effective respiration, and conditions like emphysema and pulmonary fibrosis can impair their function.
Comparison of Bacterial Causes
Streptococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae are two significant bacteria causing pneumonia. Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive bacterium commonly associated with community-acquired pneumonia, while Klebsiella pneumoniae is a Gram-negative bacterium often linked to hospital-acquired infections and known for its antibiotic resistance. Treatment strategies differ due to their unique characteristics and resistance profiles.
Pneumonia Symptoms
Common symptoms of pneumonia include cough, fever, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, muscle pain, headache, confusion, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. The severity and presentation of symptoms can vary based on the individual's age and overall health.
Recent Developments
In December 2019, a novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) was identified in Wuhan, China, leading to pneumonia cases with limited clinical information available initially. Studies have shown common symptoms and laboratory findings among affected patients, highlighting the ongoing need for research and surveillance.
Treatment Modalities
Treatment for pneumonia includes antibiotics for bacterial infections, antiviral medications for viral causes, and antifungal treatments for fungal pneumonia. Supportive care, hospitalization for severe cases, and vaccination are also critical components of managing pneumonia effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Symptoms include cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
- Various organisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
- It can range from mild to life-threatening, particularly affecting vulnerable populations.
- Treatment depends on the type and severity of pneumonia, including antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals.
- Vaccines are available to prevent certain types of pneumonia.
- Good hygiene and a healthy lifestyle can help prevent pneumonia.
- Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs essential for gas exchange.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae are significant bacterial causes of pneumonia.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae is Gram-positive and commonly associated with community-acquired pneumonia.
- Klebsiella pneumoniae is Gram-negative, often linked to hospital-acquired infections, and is known for antibiotic resistance.
- Penicillin, discovered by Alexander Fleming, revolutionized the treatment of bacterial pneumonia.
- Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease characterized by damaged and scarred lung tissue, leading to breathing difficulties.
- Common pneumonia symptoms include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
- The 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) caused a pneumonia outbreak in Wuhan, China, in December 2019.
```
Additional Concepts
Questions and Answers
What is pneumonia?
What are alveoli?
Who discovered penicillin?
What is the difference between Streptococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae?
What is pulmonary fibrosis?
What are common treatments for pneumonia?
What is an interesting fact about pneumonia?
Flashcards
What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus, causing symptoms such as cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
What are alveoli?
Alveoli are tiny air sacs in the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs, crucial for effective respiration.
Who discovered penicillin?
Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928 when he observed that a mold called Penicillium notatum killed surrounding bacteria.
What are the common symptoms of pneumonia?
Common symptoms of pneumonia include cough, fever, shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, and muscle pain.
What is the difference between Streptococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a Gram-positive bacterium commonly associated with community-acquired pneumonia, while Klebsiella pneumoniae is a Gram-negative bacterium often linked to hospital-acquired infections and known for its antibiotic resistance.
What is pulmonary fibrosis?
Pulmonary fibrosis is a lung disease characterized by damaged and scarred lung tissue, leading to difficulty in breathing and reduced oxygen exchange.
What treatments are available for pneumonia?
Treatments for pneumonia may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, antiviral medications for viral pneumonia, antifungal treatments for fungal pneumonia, and supportive care such as oxygen therapy and hydration.
What role do vaccines play in pneumonia prevention?
Vaccines, such as the pneumococcal and influenza vaccines, are critical in reducing the risk of pneumonia, especially in high-risk groups like the elderly and young children.
What historical significance does pneumonia have?
Pneumonia was once referred to as 'the old man's friend' because it often provided a relatively peaceful death for elderly patients suffering from more painful conditions.